Prostatitis and its Various Treatment Methods
Home Surgery Tips Prostatitis and its Various Treatment MethodsProstatitis and its Various Treatment Methods
Prostatitis causes pain, urinary incontinence, and difficulty in urination and is treated with medications and lifestyle changes.
Prostatitis and its Various Treatment Methods
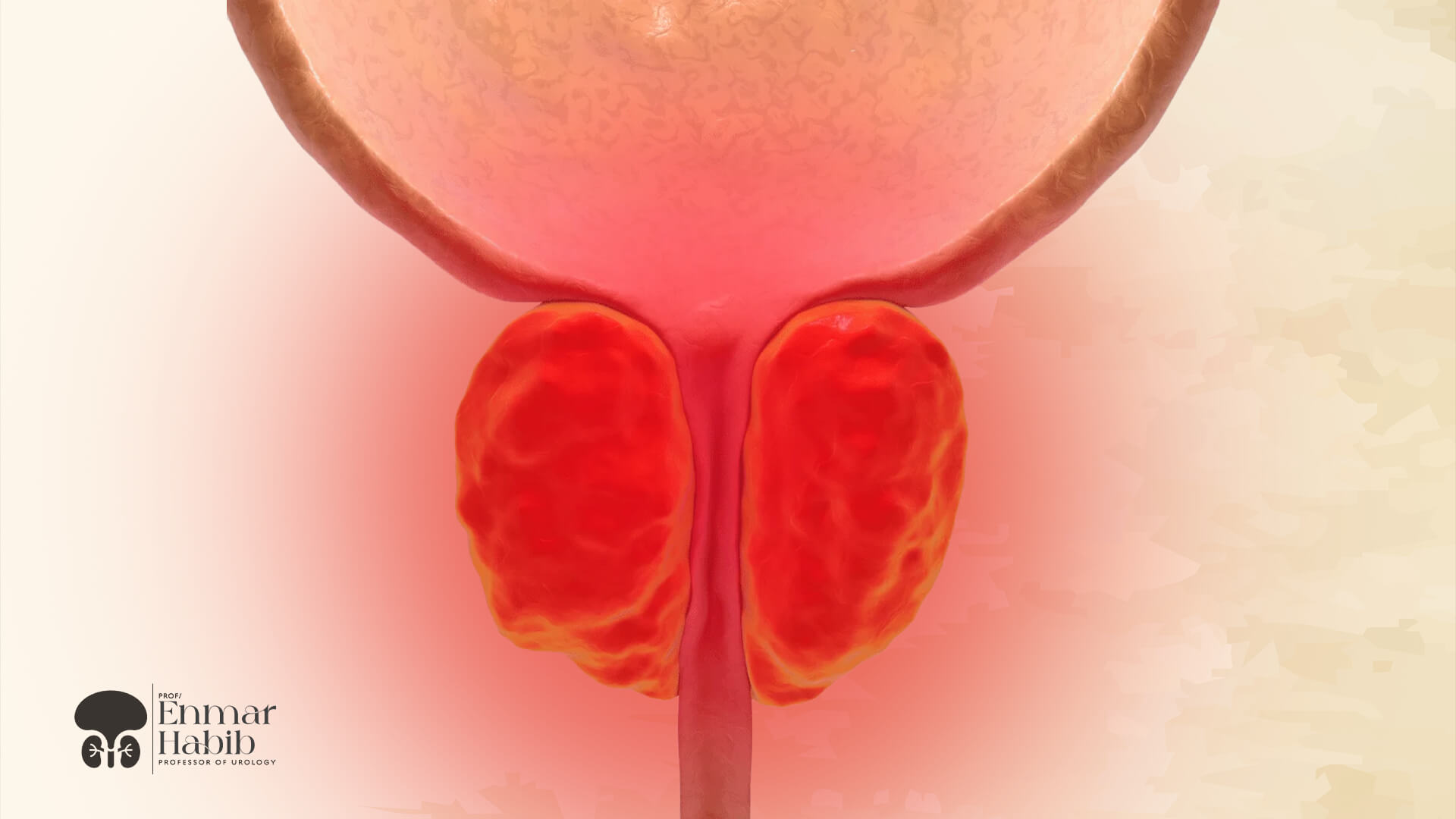
Prostatitis, or prostate congestion, is a common medical condition that affects the prostate gland, a small gland located below the bladder and in front of the rectum through which the urethra passes, forming an important part of the male reproductive system. Prostatitis is an irritation of the prostate tissue and a spasm in the pelvic muscles; this causes a range of annoying symptoms, such as an urgent need to urinate, and may significantly affect the patient's life. Learn about prostatitis and treatment methods with Dr. Enmar Mohamed Habib, Professor of Urology and Pediatric Urology at Cairo University and Fellow of McGill University, Canada.
What is prostatitis?
Prostatitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the prostate. Prostatitis is categorized into different types depending on the cause, duration, and symptoms:1. Acute prostatitis: It is caused by an acute bacterial infection. Symptoms often appear suddenly and include severe pelvic pain, difficulty urinating, fever, and pain during intercourse.
2. Chronic prostatitis: It is a persistent inflammation of the prostate that lasts for a long time (more than 3 months). Symptoms may be less severe compared to acute prostatitis, but they significantly affect the quality of life, such as pain in the lower back or pelvic area and difficulty urinating.
Chronic prostatitis may be either bacterial or non-bacterial, which is a type of prostatitis that is not associated with a bacterial infection.
Symptoms of prostatitis:
Symptoms depend on the age of the patient. At the age of 20 to 40 years, symptoms of inflammation or irritation of the prostate occur without symptoms of prostate enlargement. The most important symptom of prostatitis is bladder irritation, which manifests as:1. Frequent urge to urinate: The patient feels a sudden and strong urge to urinate at frequent intervals, even if the amount of urine is small. This urge can be annoying and affect your daily comfort.
2. Inability to retain urine for a long time: The patient has difficulty delaying urination or retaining urine for a long time, causing the need to urinate frequently throughout the day.
3. Reduced bladder control (urinary incontinence): In some cases, the patient losses complete control over urination, which can lead to involuntary urine leakage, especially when coughing or sneezing.
4. Frequent nocturia: The patient feels the need to urinate several times during the night, forcing him to wake up every hour or two, which affects the sleep quality and increases fatigue during the day.
5. Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying: Even after urination, the patient continues to feel as though the bladder has not been fully emptied. This causes a sensation of heaviness and discomfort in the pelvic area.
Causes of prostatitis:
The main cause of prostatitis is prolonged sexual arousal without ejaculation. When a man feels sexually stimulated for long periods without ejaculation, the prostate becomes congested due to the accumulation of semen in the gland, causing swelling and irritation in the prostate. Persistent congestion leads to an increase in blood pressure inside the prostate, increasing the chance of inflammation.Diagnosis of prostatitis:
Diagnosing prostatitis requires a thorough examination by a urologist. The diagnostic steps include the following:1. Medical history and clinical examination: This involves listening to the patient's symptoms and reviewing the medical history.
2. Urine analysis: To detect the presence of bacterial infection, blood, or inflammatory cells.
3. Urine and semen culture: To identify the type of bacteria causing the infection in cases of bacterial prostatitis, thus allowing for the determination of the most effective antibiotic for the condition.
Prostatitis treatments:
Prostatitis treatment varies depending on the type and cause of the condition. Here are some common treatments:1. Pharmaceutical therapy:
• Antibiotics: If prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics are the primary treatment. Antibiotics may be prescribed for 4 to 6 weeks in the case of chronic prostatitis.• Anti-inflammatories: Such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and inflammation.
• Alpha blockers: These medications help relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder, making it easier to urinate and relieving symptoms.
• Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications: In cases of non-bacterial prostatitis, psychiatric medications may be helpful to reduce stress and improve symptoms.
2. Lifestyle Changes:
Changing lifestyle habits aims to prevent the underlying cause, which is prolonged sexual arousal without ejaculation. Additionally, protection from cold exposure or constipation can help minimize symptoms.Dr. Enmar Mohamed Habib, Professor of Urology and Pediatric Urology at Cairo University and Fellow of McGill University, Canada, explains that prostatitis, if diagnosed early, can be successfully treated. He also points out the importance of consulting the doctor as soon as any symptoms similar to those mentioned above appear for early diagnosis and prevention of potential complications.